3.1. Priority Queue ¶
- In computer science/data structures, a priority queue is an abstract data type which is like a regular queue or stack data structure, but where additionally each element has a "priority" associated with it. In a priority queue, an element with high priority is served before an element with low priority. If two elements have the same priority, they are served according to their order in the queue.
- While priority queues are often implemented with heaps, they are conceptually distinct from heaps. A priority queue is an abstract concept like "a list" or "a map"; just as a list can be implemented with a linked list or an array, a priority queue can be implemented with a heap or a variety of other methods such as an unordered array.
- 출처 : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue
3.2. Priority Queue in STL ¶
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<ctime>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue <int> pq;
int v[100];
int main(void)
{
int n = 10;
srand(time(NULL));
printf("Vector \n");
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
v[i] = rand() % 100;
printf("%d ", v[i]);
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
pq.push(v[i]);
}
printf("Priority Queue \n");
while(!pq.empty()){
printf("%d ", pq.top());
pq.pop();
}
printf("\n\n");
}
3.3. Heap ¶
- 힙(Heap)은 특별한 트리를 기본으로 한 자료구조(tree-based structure)로서 다음과 같은 heap 속성(property)을 만족한다.
- A가 B의 부모노드(parent node) 이면, 힙(heap) 에 적용된 것과 같은 순서로 key(B)에 관해서 key(A)는 순서가 정해진다.
- 각 노드의 children 의 최대개수는 heap 의 종류에 따라 다르지만, 많은 타입에서 children 의 개수는 2개 이하이다. 그리고 이것은 이진 힙(binary heap)으로 알려져 있다.
- 출처 : http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%9E%99_(%EC%9E%90%EB%A3%8C_%EA%B5%AC%EC%A1%B0)
- Heap Visualization - http://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Heap.html
- A heap data structure should not be confused with the heap which is a common name for the pool of memory from which dynamically allocated memory is allocated. The term was originally used only for the data structure.
3.4.1. Property ¶
- Shape property
The tree is a complete binary tree; that is, all levels of the tree, except possibly the last one (deepest) are fully filled, and, if the last level of the tree is not complete, the nodes of that level are filled from left to right.
- Heap property
All nodes are either greater than or equal to or less than or equal to each of its children, according to a comparison predicate defined for the heap.
3.4.2. Operation ¶
- Max Heap 이라고 가정하자.
- 삽입
- 가장 마지막 위치에 원소를 삽입한다.
- 삽입 한 원소를 원소의 부모와 비교한다. 만약 부모가 더 크다면 멈춘다.
- 부모가 더 작다면, 부모와 위치를 바꾼다. 그리고 다시 그 위치에서 부모와 비교...
- 가장 마지막 위치에 원소를 삽입한다.
- 삭제
- Root의 원소를 제거하고, Root에 Heap에 가장 마지막 위치에 있는 원소를 놓는다.
- 새로운 Root와 Root의 자식과 비교한다. 만약 Root가 더 크다면 멈춘다.
- Root가 더 작다면, 자식과 위치를 교체한다. 그리고 다시 그 위치에서 자식과 비교...
- Root의 원소를 제거하고, Root에 Heap에 가장 마지막 위치에 있는 원소를 놓는다.
3.5. Heap Sort ¶
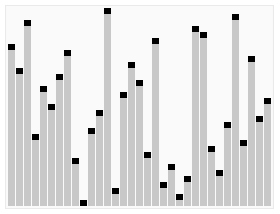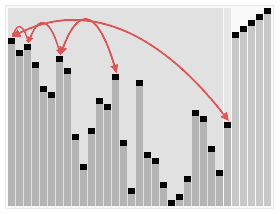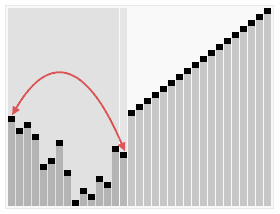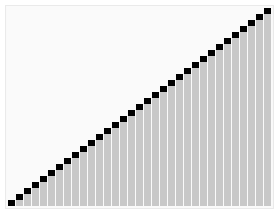
[GIF image (274.43 KB)]
- 간단한 설명 : http://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%ED%9E%99_%EC%A0%95%EB%A0%AC
- Heap Sort Visualization - http://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/HeapSort.html
3.6. Application of Priority Queue ¶
- Dijkstra's algorithm : 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘인데 그래프 시간에 배웁니다.
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm#Using_a_priority_queue
- Best-first search algorithms
- Prim's algorithms
- 그 외에도 여러가지 등등등..
4. 후기 ¶
- 주제를 하나를 잡고 설명하려니까 편하네요. 피드백을 받아서 개선을 해보려고 하는데 개선이 되는지는 잘 못느끼겠네요. 좀 더 피드백을 주었으면 합니다. 더 좋은 새싹 교실이 될 수 있도록 하고 싶네요. 강사나 학생에게나 시간 낭비가 되지 않는 새싹이 되었으면 합니다. 다음 주는 Map과 Binary Search Tree를 가르칠 계획입니다. Floyd Algorithm까지는 갈 길이 머네요. 올 해가 가기 전에는 마무리 해야 될텐데... - 권영기
- 뭔가 늘어납니다! 재귀만 보면 머리가 아파오는 저가 이걸 제대로 따라갈수 있을지 걱정입니다. 넘어아 할 사이니 이번기회에 극복해보는걸로, 쿨럭










