Difference between r1.1 and the current
@@ -52,7 +52,10 @@
=== 이동 횟수에 관한 공식 ===
기둥이 K개일 때의 하노이 탑 문제를 HANOI-K라고 명명하자. 옮길 블록의 갯수는 N이다. (여기서 K는 3 이상의 정수, N은 자연수)
기둥이 K개일 때의 하노이 탑 문제를 HANOI-K라고 명명하자. 옮길 블록의 갯수는 N이다. (여기서 K는 3 이상의 정수, N은 자연수)
* 점화식
* 점화식
* 계산량은 O(N)
attachment:HANOI-K_점화식_2.png
* 닫힌 형태
* 닫힌 형태
* 거듭제곱을 구할 때 Divide & Conquer를 적용하면 계산량은 O(logN)
attachment:HANOI-K_닫힌형태.png
직접 플레이하는 버전 ¶
블록 개수 입력하면 이동 순서 출력하는 버전 ¶
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int count = 0;
void hanoi(int blocks[], int i, int goal) {
int rest;
if (i == 0){
printf("%d: %d -> %d\n", i, blocks[i], goal);
blocks[i] = goal;
count++;
}
else if (blocks[i - 1] == blocks[i]){
rest = 3 - blocks[i] - goal;
hanoi(blocks, i - 1, rest);
hanoi(blocks, i, goal);
hanoi(blocks, i - 1, goal);
}
else{
printf("%d: %d -> %d\n", i, blocks[i], goal);
blocks[i] = goal;
count++;
}
}
void main() {
int numBlocks=0, j;
int *blocks = NULL;
while (1){
printf("Enter the number of blocks: ");
if (scanf_s("%d", &numBlocks) == 0 || numBlocks < 3){
fflush(stdin);
puts("You must input an integer n >= 3");
continue;
}
count = 0;
if (blocks != NULL) free(blocks);
blocks = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numBlocks);
for (j = 0; j < numBlocks; j++) blocks[j] = 0;
hanoi(blocks, numBlocks - 1, 2);
printf("move count: %d\n", count);
}
}
이동 횟수에 관한 공식 ¶
기둥이 K개일 때의 하노이 탑 문제를 HANOI-K라고 명명하자. 옮길 블록의 갯수는 N이다. (여기서 K는 3 이상의 정수, N은 자연수)
- 점화식
- 계산량은 O(N)
- 계산량은 O(N)
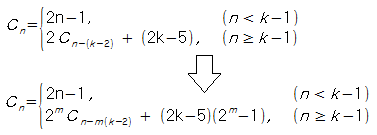
[PNG image (4.62 KB)]
- 닫힌 형태
- 거듭제곱을 구할 때 Divide & Conquer를 적용하면 계산량은 O(logN)
- 거듭제곱을 구할 때 Divide & Conquer를 적용하면 계산량은 O(logN)
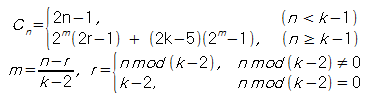
[PNG image (3.55 KB)]










