Contents
1. Nand2Tetris ¶
- мҠӨн„°л”” мҶҢк°ң :
- м»ҙн“Ён„°мқҳ мөңн•ҳмң„ л ҲлІЁ кі„мёөмқё л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎң(н•ҳл“ңмӣЁм–ҙ)лӢЁл¶Җн„° OSмҷҖ high level languageк№Ңм§Җ л‘җлЈЁл‘җлЈЁ м„ӯл өн•ҳкі мӢӨмҠөн•ҳм—¬ мөңмў…м—җлҠ” н…ҢнҠёлҰ¬мҠӨлҘј л§Ңл“ңлҠ”кІғмқҙ лӘ©н‘ңмқё мҠӨн„°л””мһ…лӢҲлӢӨ.
- м»ҙн“Ён„°мқҳ мөңн•ҳмң„ л ҲлІЁ кі„мёөмқё л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎң(н•ҳл“ңмӣЁм–ҙ)лӢЁл¶Җн„° OSмҷҖ high level languageк№Ңм§Җ л‘җлЈЁл‘җлЈЁ м„ӯл өн•ҳкі мӢӨмҠөн•ҳм—¬ мөңмў…м—җлҠ” н…ҢнҠёлҰ¬мҠӨлҘј л§Ңл“ңлҠ”кІғмқҙ лӘ©н‘ңмқё мҠӨн„°л””мһ…лӢҲлӢӨ.
- мҠӨн„°л””м—җ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳлҠ” мӮ¬мқҙнҠё -> http://www.nand2tetris.org/
1.1. 9/26(лӘ©мҡ”мқј) ¶
- м°ём—¬мһҗ : к№ҖмңӨнҷҳ, м•ҲнҳҒмӨҖ, к¶ҢмҳҒкё°.
- мҠӨн„°нӢ°м—җ лҢҖн•ң л°©н–Ҙ :
- лҲ„к°Җ : 3лӘ… + a(?)к°Җ
- мқёмӣҗмҲҳ л¬ём ң : max 5лӘ…к№Ңм§Җ л°ӣлҠ”лӢӨ.
- мқёмӣҗмҲҳ л¬ём ң : max 5лӘ…к№Ңм§Җ л°ӣлҠ”лӢӨ.
- лҲ„к°Җ : 3лӘ… + a(?)к°Җ
- м–ём ң : мӢңмһ‘мқҖ? мқҙлІҲмЈјл¶Җн„° // л§ӨмЈј мқјмҡ”мқј 1мӢң
- м–ҙл””м„ң : zpмӢӨм—җм„ң
- л¬ҙм—Үмқ„ : nand2TerisлҘј
- м–ҙл–»кІҢ : 집м—җм„ң pptлҘј мқҪм–ҙмҳЁл’Ө л§ҢлӮҳм„ң мӢӨмҠөн•ҳлҠ” л°©н–ҘмңјлЎң.
- мҷң :
- нҳҒмӨҖ ->мһ¬лҜёмһҲмқ„кІғк°ҷм•„м„ң.
- мңӨнҷҳ ->м»ҙн“Ён„° мһҗмІҙлҘј м•„лҠ” мўӢмқҖ кё°нҡҢлқјкі мғқк°Ғн•ҙм„ң + нқҘлҜёк°Җ мһҲлҠ” 분야? м—¬м„ң.
- мҳҒкё° ->м „мІҙлҘј кҝ°лҡ«кё°мң„н•ҙ.
- нҳҒмӨҖ ->мһ¬лҜёмһҲмқ„кІғк°ҷм•„м„ң.
- лӢӨмқҢмӢңк°„к№Ңм§Җ н• мқј : chapter 0,1 мқҪм–ҙмҳӨкё°.
1.2.1. кіөл¶Җн•ң лӮҙмҡ© ¶
- Chapter1
- кё°ліём Ғмқё л…јлҰ¬ кІҢмқҙнҠёлҘј кіөл¶Җн•Ё.
- Nand gateлҘј primitive gateлЎң лҶ“кі , лӮҳлЁём§Җ л…јлҰ¬ кІҢмқҙнҠё Not, And, Or, Xor, Mux, Demux л“ұмқ„ Nandл§ҢмңјлЎң кө¬нҳ„.
- MuxлӮҳ Demuxк°ҷмқҖ кІҪмҡ°, мһ…л ҘмқҙлӮҳ м¶ңл Ҙмқҙ л„Ҳл¬ҙ л§Һмқ„ кІҪмҡ°, мһ‘мқҖ к·ңлӘЁмқҳ MuxлҘј м—¬лҹ¬ к°ң мқҙмҡ©н•ҙм„ң нҒ° к·ңлӘЁмқҳ MuxлҘј кө¬нҳ„н•ҙлҸ„ лҗңлӢӨ. мҳҲлҘј л“Өл©ҙ, 4way MuxлҠ” 2Way Mux 3к°ңлҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҙм„ң кө¬нҳ„н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ.
- HDL Code
- Not Gate
CHIP Not2 {
IN a;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = a, b = a, out = out);
}
- And Gate
CHIP And {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = a, b = b, out = x);
Nand(a = x, b = x, out = out);
}
- Or Gate
CHIP Or {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = a, b = a, out = x1);
Nand(a = b, b = b, out = x2);
Nand(a = x1, b = x2, out = out);
}
- Xor Gate
CHIP Xor {
IN a, b;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = a, b = a, out = nota);
Nand(a = b, b = b, out = notb);
Nand(a = nota, b = b, out = x1);
Nand(a = a, b = notb, out = x2);
Nand(a = x1, b = x2, out = out);
}
- Mux
CHIP Mux {
IN a, b, s;
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = s, b = s, out = nots);
Nand(a = a, b = s, out = x1);
Nand(a = b, b = nots, out = x2);
Nand(a = x1, b = x2, out = out);
}
- Mux 4way
CHIP Mux4way {
IN a[4], s[2];
OUT out;
PARTS:
Nand(a = s[0], b = s[0], out = nots0);
Nand(a = s[1], b = s[1], out = nots1);
Nand(a = a[0], b = s[1], out = x0);
Nand(a = a[1], b = nots1, out = x1);
Nand(a = a[2], b = s[1], out = x2);
Nand(a = a[3], b = nots1, out = x3);
Nand(a = x0, b = x1, out = xx0);
Nand(a = x2, b = x3, out = xx1);
Nand(a = xx0, b = s[0], out = xxx0);
Nand(a = xx1, b = nots0, out = xxx1);
Nand(a = xxx0, b = xxx1, out = out);
}
- Demux
DemuxлҠ” лӢӨ кө¬нҳ„н•ҳкі м„ң Mux 4wayлҘј Demux нҢҢмқјм—җ мҚЁлІ„лҰ¬лҠ” л°”лһҢм—җ лӮ л ӨлІ„лҰј г…Ўг…Ў;
1.2.3. нӣ„кё° ¶
- мҮ лҝ”лҸ„ лӢЁк№Җм—җ л№јлқјлҠ” л§җмқҙ мһҲл“Ҝмқҙ, мҲңмӢқк°„м—җ мҠӨн„°л”” 진н–үн•©лӢҲлӢӨ. н•ҷкё° лҒқлӮ л•Ңк№Ңм§Җ л§ӨмЈј 진н–үн•ҙліҙл Өкі н•ҳлҠ”лҚ°, лҒқк№Ңм§Җ лӢӨ н• мҲҳ мһҲм—Ҳмңјл©ҙ мўӢкІ мҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. лӯҗ мңӨнҷҳмқҙлӮҳ нҳҒмӨҖмқҙнҳ• мһҲмңјлӢҲк№Ң мһҳ 진н–үлҗҳкІ мЈ . мқҙлІҲ мӢңк°„м—җ н–ҲлҚҳ кІғмқҖ кё°мҙҲ мӨ‘м—җ кё°мҙҲмқёлҚ°, мӮ¬мӢӨ мһ‘л…„ л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎң мӢңк°„м—җ Nand кІҢмқҙнҠёлЎң лӢӨлҘё gate кө¬нҳ„н•ҳкё° л”°мң„лҠ” н•ҙліём Ғмқҙ м—Ҷм–ҙм„ң мўҖ лӢ№нҷ©лҸ„ н–ҲмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. к·ёлҰ¬кі к·ёлҰј к·ёлҰ¬лҠ” кІғлҸ„ м°ё к°„л§Ңмқҙкі , лӢӨмқҢ мӢңк°„к№Ңм§Җ л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎң ppt мўҖ ліҙкі м„ң мҷҖм•јкІ л„Өмҡ”. к°„лӢЁн•ң 4way MUXлҸ„ м ҖлҰ¬ кёҙлҚ°, мӮ¬м№ҷм—°мӮ°мқҖ м–ҙл–»кІҢ н•ҙм•јн• м§Җ.. лЁёлҰ¬к°Җ м•„н”•лӢҲлӢӨ. - к¶ҢмҳҒкё°
- к°„л§Ңм—җ л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎңлҘј лӢӨлЈЁл©ҙм„ң лӮҙк°Җ к№ҢлЁ№кі мһҲлҚҳ л¶Җ분мқҙ л§ҺлӢӨкі лҠҗлӮҢлӢҲлӢӨ. л¬јлЎ м¶”мғҒнҷ”лқјлҠ” мўӢмқҖ л…Җм„қмқҙ мһҲм–ҙм„ң мҡ°лҰ¬к°Җ лӘЁл“ кІғмқ„ кё°м–өн• н•„мҡ”лҠ” м—Ҷм§Җл§Ң, к·ёлһҳлҸ„ мӣҗлҰ¬лҘј м•ҲлӢӨкі н•ҙм„ң м•ҲмўӢмқ„ кІғ м—Ҷмқ„л“Ҝн•ҳл„Өмҡ”. nandлЎң мӢңмһ‘н•ҙм„ң nandлЎң лҒқлӮҳлҠ” мӢңк°„мқҙм—ҲмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. - м•ҲнҳҒмӨҖ
- м§ҖкёҲмқҖ мІҳмқҢл¶Җ분мқҙлқј л¬ҙлӮңн•ҳкІҢ 진н–үн–Ҳм§Җл§Ң... к°Җл©ҙк°ҲмҲҳлЎқ м–ҙл–ӨмӢқмңјлЎң 진н–үлҗ м§Җ лӮңмқҙлҸ„м—җ л”°лқјм„ң мҷ м§Җ л°”лҖ”мҲҳлҸ„ мһҲмңјл ӨлӮҳ...н•ҳлҠ” мғқк°Ғмқҙ л“Өм—ҲмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. к·ёлӮҳм ҖлӮҳ л…јлҰ¬нҡҢлЎң л’·л¶Җ분мқҖ кұ°мқҳ кё°м–өмқҙ м—ҶлҠ”лҚ°... м „кіөмұ…н•ңлІҲ нӣқм–ҙліҙкі мҷҖм•јн• кІғк°ҷмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. - к№ҖмңӨнҷҳ
1.3.1. кіөл¶Җ лӮҙмҡ© ¶
- half-adder, full-adder, 16bit-adder, incremental adder, ALUм—җ лҢҖн•ҙм„ң кіөл¶Җн•ҳкі кө¬нҳ„н•ҳмҳҖмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ.
- Half-Adder
CHIP HalfAdder {
IN a, b; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b
carry; // Left bit of a + b
PARTS:
And(a = a, b = b, out = carry);
Xor(a = a, b = b, out = sum);
}
- Full-Adder
CHIP FullAdder{
IN a, b, c; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b + c
carry; // Left bit of a + b + c
PARTS:
// Put you code here:
Xor(a=a, b=b, out=s1);
And(a=a, b=b, out=c1);
Xor(a=s1, b=c, out=sum);
And(a=s1, b=c, out=c2);
Or(a=c1, b=c2, out=carry);
}
- 16bit Adder
CHIP Add16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
FullAdder(a = a[0], b = b[0], c = false, sum = out[0], carry = c1);
FullAdder(a = a[1], b = b[1], c = c1, sum = out[1], carry = c2);
FullAdder(a = a[2], b = b[2], c = c2, sum = out[2], carry = c3);
FullAdder(a = a[3], b = b[3], c = c3, sum = out[3], carry = c4);
FullAdder(a = a[4], b = b[4], c = c4, sum = out[4], carry = c5);
FullAdder(a = a[5], b = b[5], c = c5, sum = out[5], carry = c6);
FullAdder(a = a[6], b = b[6], c = c6, sum = out[6], carry = c7);
FullAdder(a = a[7], b = b[7], c = c7, sum = out[7], carry = c8);
FullAdder(a = a[8], b = b[8], c = c8, sum = out[8], carry = c9);
FullAdder(a = a[9], b = b[9], c = c9, sum = out[9], carry = c10);
FullAdder(a = a[10], b = b[10], c = c10, sum = out[10], carry = c11);
FullAdder(a = a[11], b = b[11], c = c11, sum = out[11], carry = c12);
FullAdder(a = a[12], b = b[12], c = c12, sum = out[12], carry = c13);
FullAdder(a = a[13], b = b[13], c = c13, sum = out[13], carry = c14);
FullAdder(a = a[14], b = b[14], c = c14, sum = out[14], carry = c15);
FullAdder(a = a[15], b = b[15], c = c15, sum = out[15], carry = c16);
}
- Incremental
CHIP Inc16 {
IN a[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
FullAdder(a = a[0], b = false, c = true, sum = out[0], carry = c1);
FullAdder(a = a[1], b = false, c = c1, sum = out[1], carry = c2);
FullAdder(a = a[2], b = false, c = c2, sum = out[2], carry = c3);
FullAdder(a = a[3], b = false, c = c3, sum = out[3], carry = c4);
FullAdder(a = a[4], b = false, c = c4, sum = out[4], carry = c5);
FullAdder(a = a[5], b = false, c = c5, sum = out[5], carry = c6);
FullAdder(a = a[6], b = false, c = c6, sum = out[6], carry = c7);
FullAdder(a = a[7], b = false, c = c7, sum = out[7], carry = c8);
FullAdder(a = a[8], b = false, c = c8, sum = out[8], carry = c9);
FullAdder(a = a[9], b = false, c = c9, sum = out[9], carry = c10);
FullAdder(a = a[10], b = false, c = c10, sum = out[10], carry = c11);
FullAdder(a = a[11], b = false, c = c11, sum = out[11], carry = c12);
FullAdder(a = a[12], b = false, c = c12, sum = out[12], carry = c13);
FullAdder(a = a[13], b = false, c = c13, sum = out[13], carry = c14);
FullAdder(a = a[14], b = false, c = c14, sum = out[14], carry = c15);
FullAdder(a = a[15], b = false, c = c15, sum = out[15], carry = c16);
}
- ALU
1.4.1. кіөл¶Җ лӮҙмҡ© ¶
- Chapter 4
- Hack Machine languageлҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҙм„ң н”„лЎңк·ёлһЁмқ„ мһ‘м„ұн•ҙ лҙ„.
D - data, A - address, M - memory
e.g. A - 32мқјкІҪмҡ°, MмқҖ M32мһ„. Mмқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н• л•Ң, Aмқҳ к°’мқҖ memoryмқҳ address
2к°ңмқҳ Instructionмқ„ м§Җмӣҗн•ңлӢӨ. к°Ғ InstructionмқҖ 2ByteмқҙлӢӨ.
- A-Instruction : @value // Where value is either a non-negative decimal number or a symbol referring to such number.
Binary : 0vvv vvvv vvvv vvvv
- C-Instruction : dest=comp;jump // Either the dest or jump fields may be empty.
// If dest is empty, the "=" is omitted;
// if jump is empty, the ";" is omitted;
- A-instruction мқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳл©ҙ, valueлҠ” Aм—җ л“Өм–ҙк°„лӢӨ.
Aмқҳ к°’мқҙ Mмқҙ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗ л•ҢлҠ”, мЈјмҶҢмқҳ м—ӯн• мқ„ н•ҳкі , DмҷҖ к°ҷмқҙ мӮ¬мҡ©н• л•ҢлҠ” к°’ к·ё мһҗмІҙлЎң мһ‘мҡ©н•Ё.
- Chapter4 мұ… лӮҙмҡ©
- PPT лӮҙмҡ©
{ comp }{dest }{jump}
Binary : 111a c1c2c3c4 c5c6d1d2 d3j1j2j3
1.4.2. мӢӨмҠө кіјм ң ¶
- мӢӨмҠө кіјм ң
- 1 ~ 100к№Ңм§Җ лҚ”н•ҳкё° (к¶ҢмҳҒкё°)
0 @100 1 M=1 2 @150 3 M=0 4 @100 5 D=M 6 @100 7 D=D-A 8 @18 9 D;JGT 10 @100 11 D=M 12 @150 13 M=D+M 14 @100 15 M=M+1 16 @4 17 0;JMP 18 @18 19 0;JMP
- л‘җ мҲҳмқҳ кіұ (к¶ҢмҳҒкё°)
//Memory[10] = A //Memory[11] = B //Memory[12] = Dest 0 @20 1 D=A 2 @10 3 M=D 4 @20 5 D=A 6 @11 7 M=D 8 @12 9 M=0 10 @11 11 D=M 12 @22 13 D;JEQ 14 @10 15 D=M 16 @12 17 M=D+M 18 @11 19 M=M-1 20 @10 21 0;JMP 22 @22 23 0;JMP
- л‘җ мҲҳмқҳ кіұ (к№ҖмңӨнҷҳ)
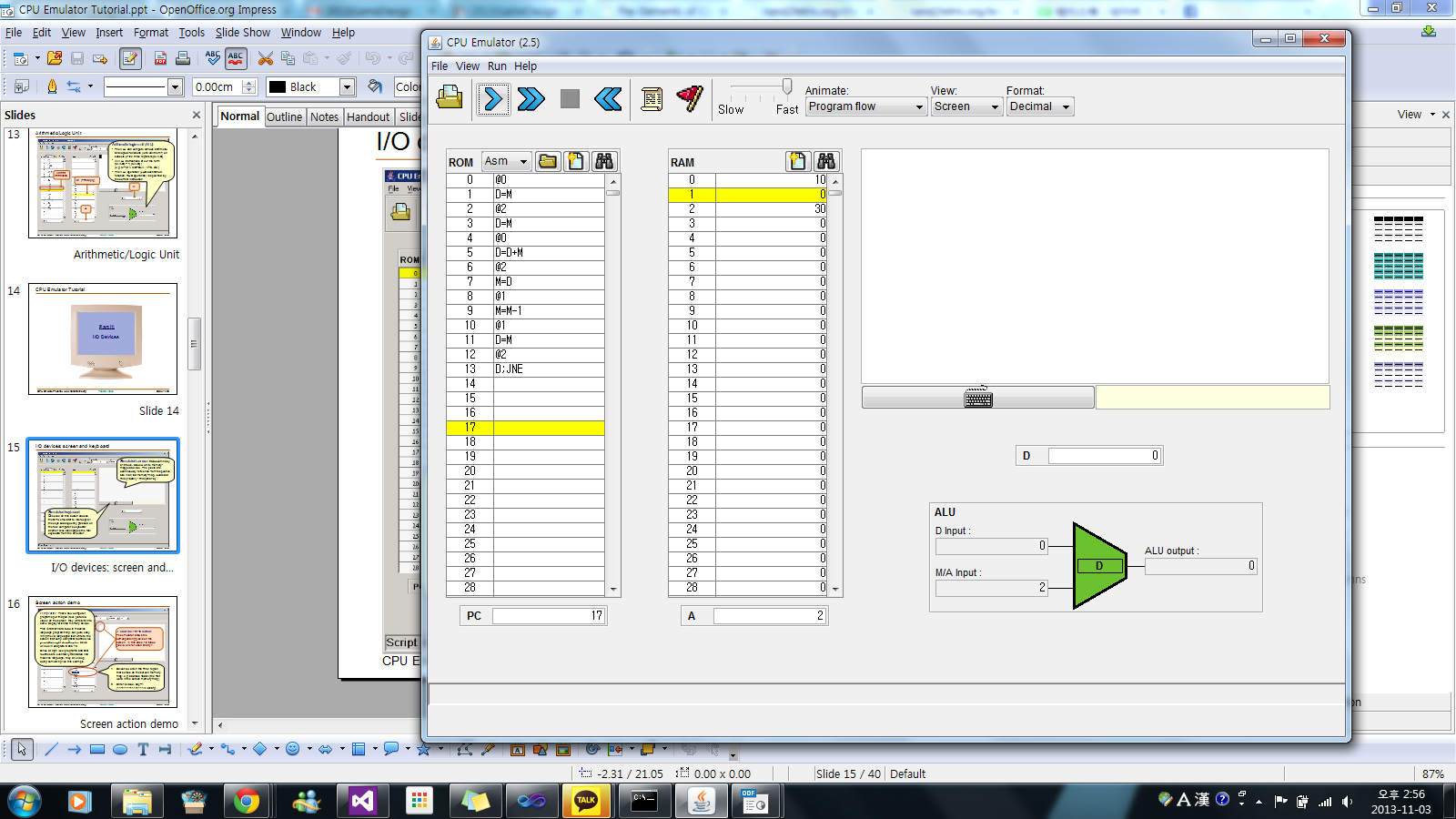
[PNG image (303.11 KB)]
- I/O Handling, (к¶ҢмҳҒкё°)(BLACKмқ„ мһ…л Ҙн•ҳл©ҙ л„ӨлӘЁк°Җ нҷ”л©ҙм—җ лӮҳмҳӨкі , WHITEлҘј мһ…л Ҙн•ҳл©ҙ нҷ”л©ҙмқҳ л„ӨлӘЁлҘј м§ҖмӣҖ)
0 @24576 1 D=M 2 @0 3 D;JEQ 4 @66 5 D=D-A 6 @1000 7 D;JEQ 8 @24576 9 D=M 10 @87 11 D=D-A 12 @2000 13 D;JEQ 14 @0 15 0;JMP 1000 @24576 1001 D=M 1002 @1000 1003 D;JEQ 1004 @76 1005 D=D-A 1006 @0 1007 D;JNE 1008 @24576 1009 D=M 1010 @1008 1011 D;JEQ 1012 @65 1013 D=D-A 1014 @0 1015 D;JNE 1016 @24576 1017 D=M 1018 @1016 1019 D;JEQ 1020 @67 1021 D=D-A 1022 @0 1023 D;JNE 1024 @24576 1025 D=M 1026 @1024 1027 D;JEQ 1028 @75 1029 D=D-A 1030 @0 1031 D;JNE 1032 @24555 1033 M=-1 1034 @0 1035 0;JMP 2000 @24576 2001 D=M 2002 @2000 2003 D;JEQ 2004 @72 2005 D=D-A 2006 @0 2007 D;JNE 2008 @24576 2009 D=M 2010 @2008 2011 D;JEQ 2012 @73 2013 D=D-A 2014 @0 2015 D;JNE 2016 @24576 2017 D=M 2018 @2016 2019 D;JEQ 2020 @84 2021 D=D-A 2022 @0 2023 D;JNE 2024 @24576 2025 D=M 2026 @2024 2027 D;JEQ 2028 @69 2029 D=D-A 2030 @0 2031 D;JNE 2032 @24555 2033 M=0 2034 @0 2035 0;JMP
- I/O Handling, (к№ҖмңӨнҷҳ)(BLACKмқ„ мһ…л Ҙн•ҳл©ҙ л„ӨлӘЁк°Җ нҷ”л©ҙм—җ лӮҳмҳӨкі , WHITEлҘј мһ…л Ҙн•ҳл©ҙ нҷ”л©ҙмқҳ л„ӨлӘЁлҘј м§ҖмӣҖ)
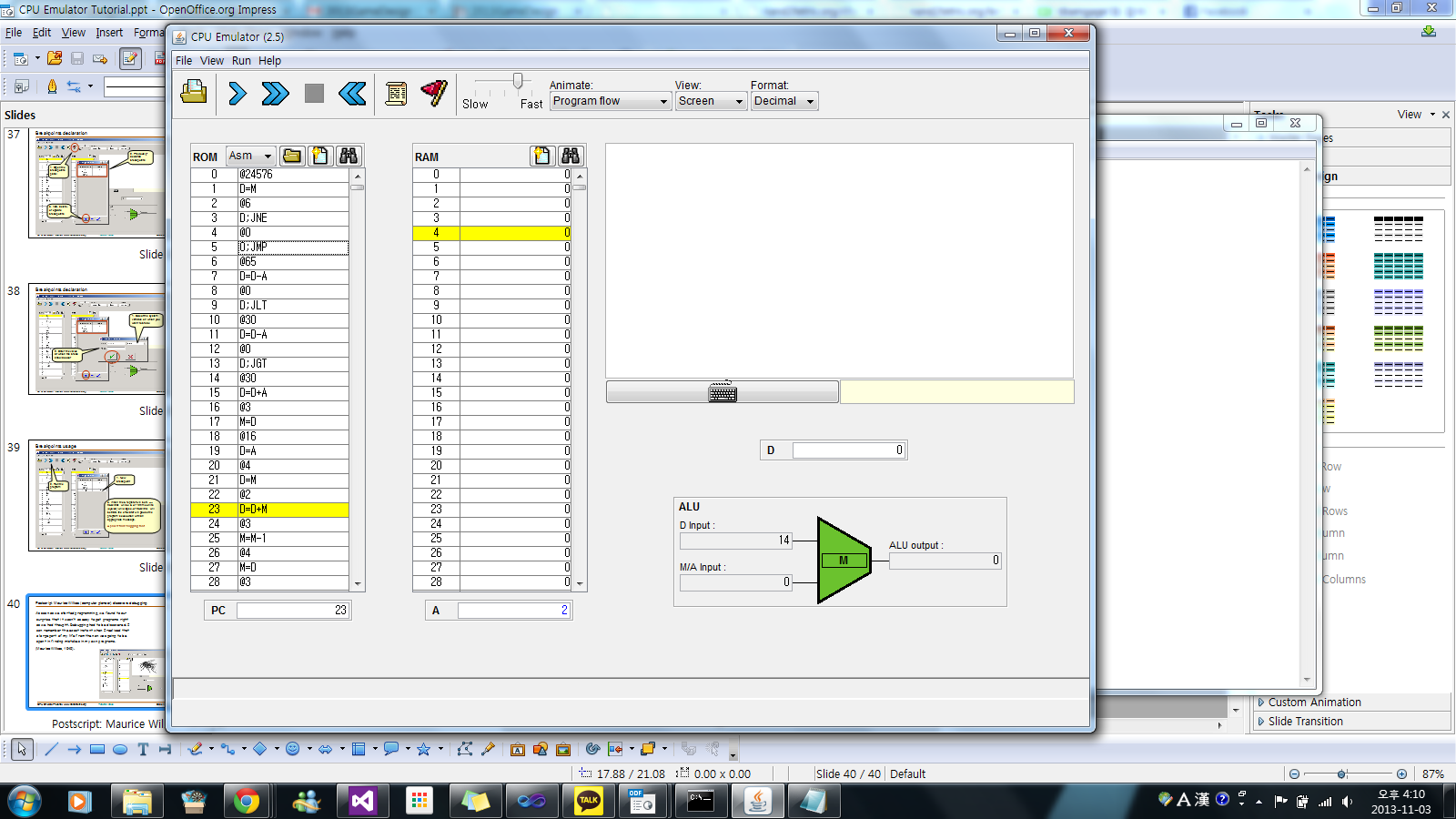
[PNG image (300.59 KB)]
1.4.3. нӣ„кё° ¶
- MIPS мҪ”л”©н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқ„ мғқк°Ғн•ҳкі кіјм ңлҘј 진н–үн–ҲлҠ”лҚ°, нҳ„мӢӨмқҖ MIPS ліҙлӢӨ лҚ” н•ҳл“ңмҪ”м–ҙн–Ҳл„Өмҡ”. SymbolлҸ„ мӮ¬мҡ©м•Ҳн•ҳкі (мӮ¬мӢӨ Cpu emulatorл§Ң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҙм„ң мғқкёҙ л¬ём ңмқј мҲҳлҸ„ мһҲм§Җл§Ң), л Ҳм§ҖмҠӨн„°лҸ„ 2~3к°ң л°–м—җ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳлҠ” мғҒнҷ©м—җм„ң мһ‘м„ұн•ҳл Өкі н•ҳлӢҲ м°ё л§үл§үн–ҲмҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. I/O Handling к°ҷмқҖ кІҪмҡ° нӮӨліҙл“ң мһ…л Ҙмқ„ н•ҙкІ°н•ҳл Өкі лӮҳлҰ„ мғқк°Ғмқ„ н•ҙм„ң мһ‘м„ұмқ„ н–ҲлҠ”лҚ°, кІ°кіјл¬јмқҙ мҳҒ л§ҲмқҢм—җ л“Өм§Җ м•ҠлҠ”кө°мҡ”. м•„л¬ҙнҠј мқҙлІҲ мӢңк°„м—җ лҠҗлӮҖ кІғмқҖ "High-Level Languageк°Җ мҷң н•„мҡ”н•ңк°Җ?" к°Җ лҗҳкІ мҠөлӢҲлӢӨ. мӮ¬мӢӨ мқҙ лҠҗлӮҢмқҖ м–ҙм…Ҳлё”лҰ¬ мӢңк°„м—җлҸ„, м»ҙн“Ён„° кө¬мЎ° мӢңк°„м—җлҸ„ лҠҗкјҲм§Җл§Ң л§җмқҙмЈ . мқҙм ң 1/3м •лҸ„лҘј 진н–үн–Ҳкі , кі„нҡҚлҢҖлЎңлқјл©ҙ 12мӣ”мқҙ лҗҳкё° м „к№Ңм§Җ 1/2лҠ” 진н–үн• мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғ к°ҷм•„м„ң 기분мқҙ мўӢл„Өмҡ”. л¬ҙмӮ¬нһҲ 진н–үн•ҙм„ң лҒқмқ„ лҙӨмңјл©ҙ н•ҳлҠ” мғқк°Ғмһ…лӢҲлӢӨ. - к¶ҢмҳҒкё°
1.5.1. кіөл¶Җ лӮҙмҡ© ¶
- Von Neumann machine (circa 1940)
Memory (data + instruction) + CPU(ALU + Registers + Control) + Input device & Output device
м§ҖкёҲк№Ңм§Җ кё°ліём Ғмқё л…јлҰ¬ кІҢмқҙнҠёлҘј (Nandл§Ң мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҙм„ң) кө¬нҳ„н•ҳкі , Combinational Chip кіј Sequential Chipк№Ңм§Җ м „л¶Җ кө¬нҳ„н–ҲлӢӨ. м§ҖкёҲк№Ңм§Җ кө¬нҳ„н•ң кІғмқ„ лӘЁл‘җ н•©м№ҳл©ҙ Computer Architectureк°Җ л§Ңл“Өм–ҙ진лӢӨ.
- The Hack Computer
A 16-bit Von Neumann platform
The instruction memory and the data memory are physically separate
Screen: 512 rows by 256 columns, black and white
Keyboard: standard
- Instruction memory(ROM)
ROMм—җлҠ” лҜёлҰ¬ л„Јм–ҙ лҶ“мқҖ н”„лЎңк·ёлһЁмқҙ мһҲмқҢ.
ROMм—җм„ңлҠ” н•ӯмғҒ 16bitмқҳ лӘ…л №м–ҙк°Җ лӮҳмҳҙ.
instruction = ROM32Kaddress
- Memory(RAM)
Data memory
мқҪкё°
k = address
out = RAMk
м“°кё°
- CPU
- Computer (мң„мқҳ лӘЁл“ logicмқ„ лӢӨ к°Җм§Җкі мһҲмқҢ)
мһҗм„ён•ң м„ӨлӘ…мқҖ architecture м—җ лӮҳмҷҖмһҲлӢӨ.
k = address
x = in
load = 1
RAMk = x
Screen(memory map)
Screenмқ„ мң„н•ң RAM м–ҙл”ҳк°ҖлҘј н• лӢ№н•ҙлҶ“мқҢ. мқҙ кіөк°„мқҖ Screenмқ„ мң„н•ң кіөк°„. CPUлҠ” к·ё кіөк°„мқ„ мқҪкұ°лӮҳ мҚЁм„ң Screen м¶ңл Ҙ
x = in
load = 1
RAMk = x
Screen(memory map)
Screenмқ„ мң„н•ң RAM м–ҙл”ҳк°ҖлҘј н• лӢ№н•ҙлҶ“мқҢ. мқҙ кіөк°„мқҖ Screenмқ„ мң„н•ң кіөк°„. CPUлҠ” к·ё кіөк°„мқ„ мқҪкұ°лӮҳ мҚЁм„ң Screen м¶ңл Ҙ
Keyboard(memory map)
KeyboardлҘј мң„н•ң RAM м–ҙл”ҳк°ҖлҘј н• лӢ№н•ҙлҶ“мқҢ. мқҙ кіөк°„мқҖ KeyboardлҘј мң„н•ң кіөк°„. CPUлҠ” к·ё кіөк°„мқ„ мқҪм–ҙм„ң м–ҙл–Ө keyк°Җ л“Өм–ҙмҷ”лҠ”м§Җ нҷ•мқё.
KeyboardлҘј мң„н•ң RAM м–ҙл”ҳк°ҖлҘј н• лӢ№н•ҙлҶ“мқҢ. мқҙ кіөк°„мқҖ KeyboardлҘј мң„н•ң кіөк°„. CPUлҠ” к·ё кіөк°„мқ„ мқҪм–ҙм„ң м–ҙл–Ө keyк°Җ л“Өм–ҙмҷ”лҠ”м§Җ нҷ•мқё.










